Reports: ND553873-ND5: Reaction Pathways for Methane on Metal Oxide Surface - Influence of Lewis Acidity and Redox Activity
Carsten Sievers, PhD, Georgia Institute of Technology
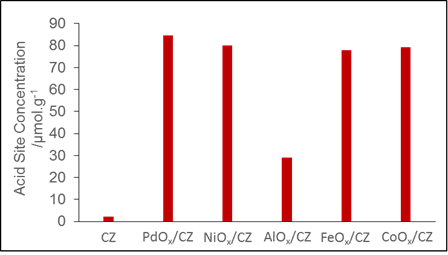
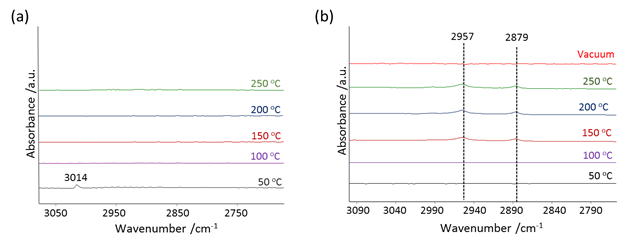
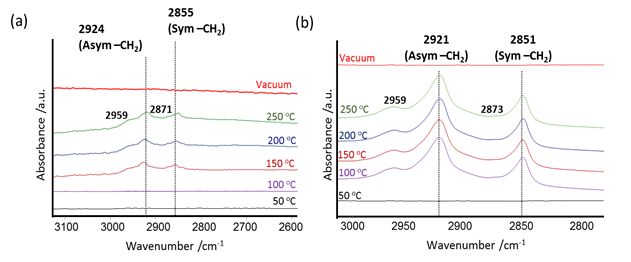
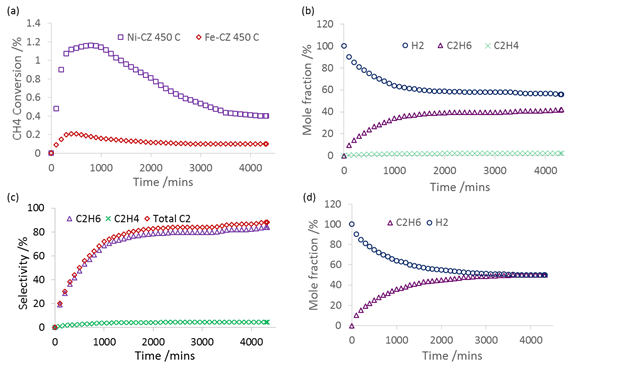
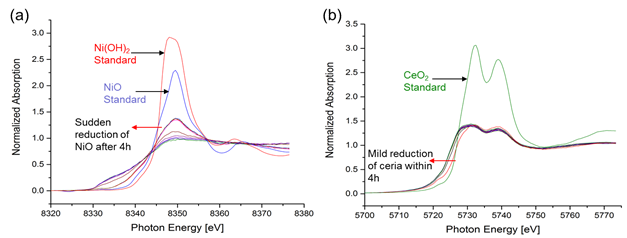
Carsten Sievers, PhD, Georgia Institute of Technology
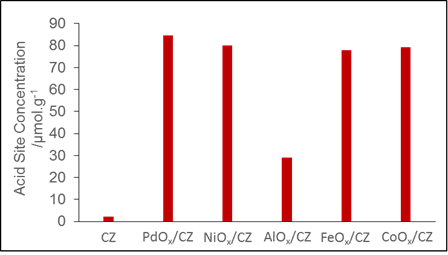




Reports in the ACS PRF Annual Report are published as submitted by the Principal Investigator.
Copyright © American Chemical Society