Reports: DNI153951-DNI1: Facile Access to Vicinal Amino-Heteroatom Functionalities from N-X Bonds
Qiu Wang, PhD, Duke University
![]()
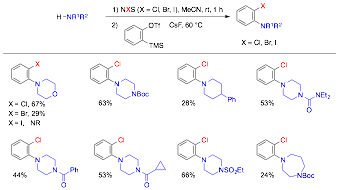
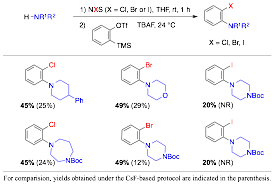
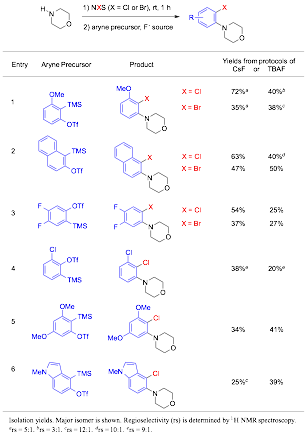

Qiu Wang, PhD, Duke University
![]()




Reports in the ACS PRF Annual Report are published as submitted by the Principal Investigator.
Copyright © American Chemical Society