Reports: DNI152782-DNI1: Direct Access of Chemically Differentiated 1,2-Diols from Oxime-Masked Mono-Alcohols
Guangbin Dong, PhD, University of Texas at Austin

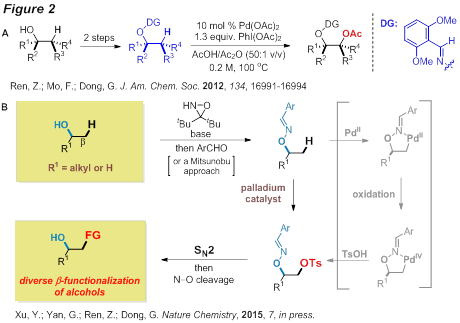
[Progress]: During the second year, significant progress has been made towards the above goal. Previously, we developed a Pd-catalyzed vicinal oxidation of unactivated C-H bonds (non-allylic/aromatic) using alcohol-derived oximes as directing groups (DG). As illustrated in Figure 2A, the oxime was employed as both a DG and an alcohol surrogate for this transformation. To enable diverse functionalization of an sp3 position that lacks pre-activation, we sought a new strategy that can directly replace a C−H bond with a good leaving group in a late-stage intermediate, and subsequently employ SN2 reactions, as a single type of transformation, for preparing derivatives or analogues (Figure 2B). To be specific, a sulfonyloxyl group can be installed at a beta C-H bond of a masked alcohol and subsequently SN2 reactions can be used to prepare various derivatives.
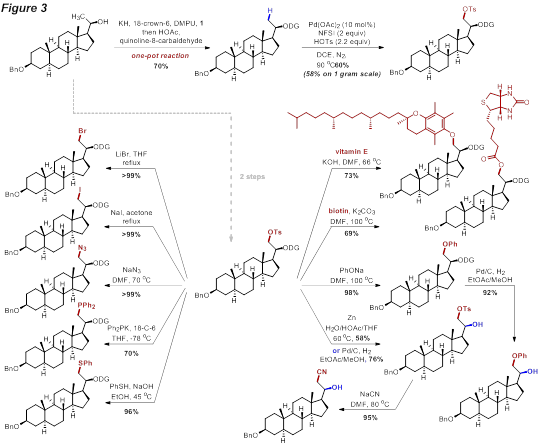
The application of this leaving group-based strategy to late-stage diversification was demonstrated on a steroid intermediate (Figure 3), in which a diverse range of novel analogues can be efficiently accessed.
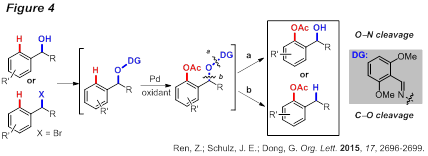
On the other hand, a Pd-catalyzed ortho-acetoxylation of masked benzyl alcohols to synthesize various 2-hydroxyalkylphenol derivatives has also been developed (Figure 4). The 2,6-dimethoxyl benzaldoxime proved to be an efficient exo-type directing group for arene (sp2) C−H functionalization. Two strategies were demonstrated to remove the directing group through N−O and C−O bond cleavages. A high catalyst turnover (>1000) was obtained to illustrate the practicality of this method.
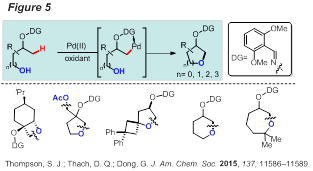
Finally, a palladium-catalyzed functionalization of unactivated sp3 C−H bonds with internal alcohol nucleophiles is also developed (Figure 5). Directed by an oxime-masked alcohol, annulation chemoselectively occurs at the beta position, leading to a range of aliphatic cyclic ethers with 4 to 7-membered rings. Tethered primary, secondary and tertiary free hydroxyl groups can all react to give the corresponding cyclized products. In addition, benzyl and silyl protected alcohols can also be directly coupled. An sp3 C−H activation/intramolecular SN2 pathway was proposed during this study.
[Significance and Impact]: Our progress has made a significant impact: (1) it disclosed a new and general mode of activity by activating alcohol beta C-H bonds; (2) it established a new strategy for introduction of diverse functional groups; (3) it would be beneficial for cyclic ether synthesis and functionalization of aromatic compounds. Current research progress laid foundation for the future work on developing diverse and general reactions for the beta-alcohol functionalization.