58th Annual Report on Research 2013 Under Sponsorship of the ACS Petroleum Research Fund
Reports: UR250759-UR2: Experimental Synthesis of Authigenic Clay Minerals: Implications for Lacustrine Deposition and Diagenesis
Daniel Deocampo, Ph.D., P.G., Georgia State University
Project Objectives
This project is using lab synthesis experiments to test several hypotheses based
on detailed studies of clay minerals in saline, alkaline lakes in East Africa
and other regions of the world (Deocampo, 2004). In these settings,
magnesium enrichment observed in ancient lake sediments has been used as an
indicator of aridity in ancient times. The recent development of high
quality geochronologically controlled stratigraphic
sections allows these geochemical indicators to be used in developing high
quality paleoenvironmental and paleoclimate
change reconstructions (Deocampo et al., 2009).
Experimental
Student Participation
Project hypotheses address 1) the
role of detrital aluminum-rich substrates on clay authigenesis;
2) aqueous silica saturation state effects on authigenesis;
3) carbonate brines, cation exchange (Ca desorption), and interstratification; 4) biogenic
CO2-induced clay dissolution; and 5) the importance of alkali concentrations on
low-temperature illitization of Fe-reduced smectite.
To test
hypothesis #1, the hydrothermal sepiolite experiments
of Wollast et al. (1968) and Mizutani
et al. (1991) are being modified by addition of an aluminum-rich detrital
component (Clay Minerals Society standard clay SWy-2). To test hypothesis
#2, synthetic brines are being formulated with varying silica concentrations,
and in contact with buffering diatomite. To test hypothesis #3, simulated
brines have been formulated (Jones et al., 1977) to test for cation exchange from calcium-saturated standard
clays. To test hypothesis #4, clay suspensions are placed in CO2-enriched
waters under ambient and high-pressure conditions.
Experimental
fluids are being monitored by AA and ICP-AES. Mineralogy is being
monitored with a new NSF-supported Panalytical X-ray diffractometer recently acquired by the project PI.
Geochemistry of 500mg separates is being determined by Rigaku
wavelength dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy, and SEM and TEM are
being used to characterize experimental materials.
In Year 2, three undergraduates
and one M.S. student were supported by the project. During
Year 2, six presentations were made at national or regional meetings of the
Geological Society of America by either currently-supported
students, or those supported in Year 1.
These include a presentation by a student who helped develop the brine
synthesis methods for this project's experiments (Yurman
and Deocampo, 2012); a student who helped develop the high-temperature Parr
bomb experimental methods (Raines and Deocampo, 2012); and preliminary tests of
hypothesis #1 (Pickering et al., 2013a), hypothesis #3 (Taylor et al., 2013),
and hypothesis #5 (Razumov et al., 2013).
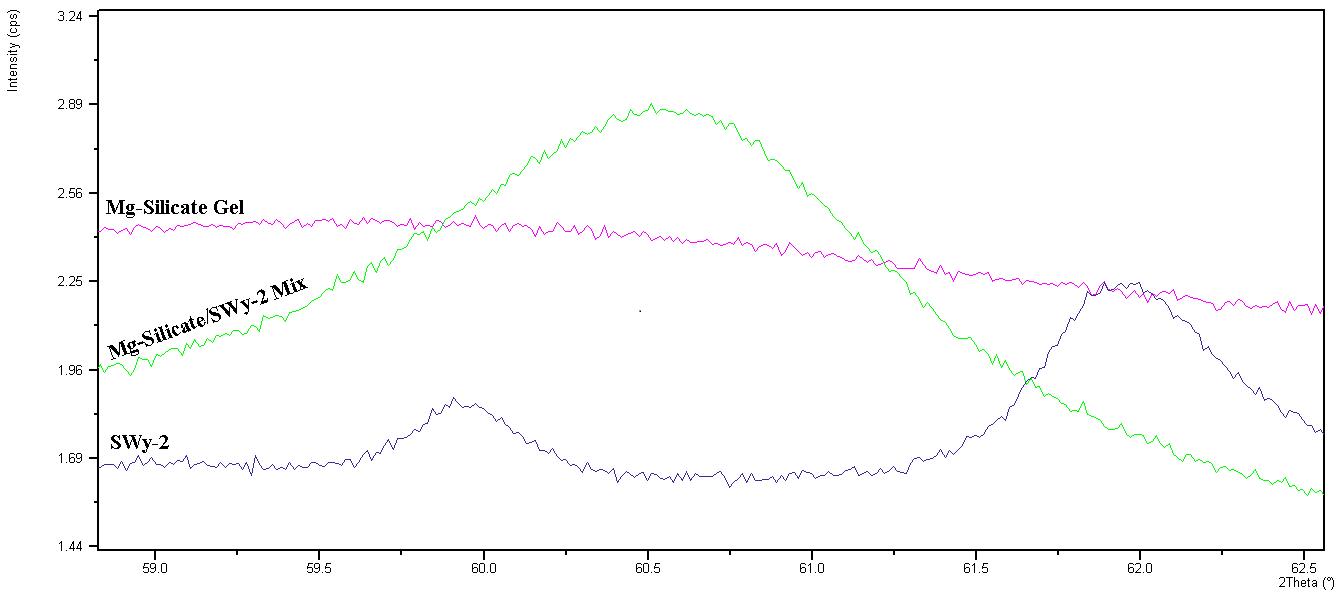
Taylor et al. (2013) showed the predicted increase in cation exchange associated with carbonate brines, a key initial step assumed to be necessary in the development of Mg-rich clay interstratifications (Deocampo et al., 2009). Razumov et al. (2013) demonstrated how brines increase the amount of K taken up to Fe-rich clays after artificial Fe-reduction, implying more effective illitization under such conditions. Pickering et al. (2013a; 2013b) showed the development of trioctahedral (Mg-rich) domains during the clay synthesis experiments (Figure 1), an important indicator of active diagenetic mineral crystallization.
Figure 1. X-ray diffractograms of clay synthesis experimental materials (Pickering and Deocampo, 2013), powdered and randomly oriented, and limited to the range of 2-theta values where 060 peaks occur attributable to the octahedral layer in sheet silicates. SWy-2 (Clay Minerals Society standard source clay) and Mg-Silicate gel patterns are raw materials, the green pattern shows the mixture of the two following thermal treatment. Subsequent analysis suggests the peak in the synthesized materials represents trioctahedral (Mg-rich) domains formed in increasingly crystalline sepiolite.
The students in the lab are now following up on these initial results, in particular exploring X-ray diffraction data indicating increases in crystallinity of synthetic products. One of the undergraduates from Year 2 of the project (Lucy Taylor) has now graduated and entered the MS program, and she is continuing to work with the project as a senior mentor for the new team of undergraduates. The group is planning to submit their results at the upcoming southeast section meeting of the Geological Society of America in Virginia.
References (*student author*)
Deocampo, D.M., 2004. Authigenic clays in East Africa: Regional trends and paleolimnology at the Plio-Pleistocene boundary, Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania. Journal of Paleolimnology, vol. 31, p. 1-9.
Deocampo, D.M., Cuadros, J., Wing-Dudek, T., Olives, J., and Amouric, M., 2009. Saline lake diagenesis as revealed by coupled mineralogy and geochemistry of multiple ultrafine clay phases: Pliocene Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania. American Journal of Science, vol. 309, p. 834-868.
*Huckins, S.*, and Deocampo, D., 2012. Carbon sequestration in northeast Georgia: potential clay dissolution in the Cambrian Weisner Quartzite (Sandstone). Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs, vol. 44, p. 62.
Jones, B.F., Eugster, H.P., and Rettig, S.L., 1977. Hydrochemistry of the Lake Magadi basin, Kenya. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, vol. 41, p. 53-72.
*Raines, J.E.*, and Deocampo, D.M., 2012. Caprock interactions with supercritical CO2 and brine: a laboratory study of the effects of simulated geological CO2 sequestration on shale's from the Black Warrior River Basin, Alabama. Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs, vol. 44, p. 395.
Mizutani, T., Fukushima, Y., Okada, A., and Kamigaito, O., 1991. Hydrothermal synthesis of sepiolite. Clay Minerals, vol. 26, p. 441-445.
*Pickering, R.A., Taylor, L.C., Razumov, P.*, and Deocampo, D.M., 2013. Role of Al-rich detritus in Mg-silicate supersaturated solutions. Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs, vol. 45, n. 2, p. 60.
*Pickering, R.A.*, and Deocampo, D.M., 2013. Tri-Octahedral domains in synthetic clays: implications for lacustrine paleoenvironmental reconstruction. Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs, vol. 45, no. 7, p. 781.
*Razumov, P., Taylor, L.C., Pickering, R.A.*, and Deocampo, D.M., 2013. Clay synthesis: Modeling the uptake of K+ during low-temperature illitization of smectite. Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs, vol. 45, n. 2, p. 12.
*Taylor, L.C., Razumov, P., Pickering, R.A.*, and Deocampo, D.M., 2013. Effects of sodium carbonate brines on cation exchange and clay interstratification. Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs, vol. 45, n. 2, p. 12.
*Yurman, S.*, and Deocampo, D.M., 2012. Carbon sequestration potential in simulated saline lake waters. Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs, vol. 44, p. 395.
Wollast, R., Mackenzie, F.T., and Bricker, O.P., 1968. Experimental precipitation and genesis of sepiolite at earth-surface conditions. American Mineralogist, vol. 53, p. 1645-1662.
Copyright © 2014 American Chemical Society