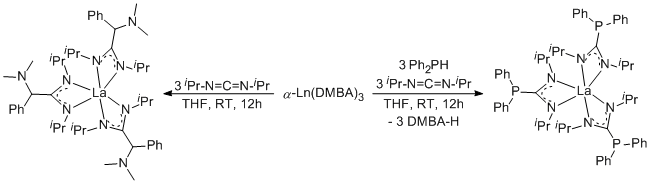
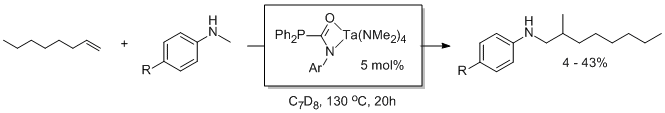
Reports: ND352709-ND3: New Homoleptic Rare-Earth Metal Complexes for Catalytic Hydrophosphination
Joseph A. R. Schmidt, PhD, University of Toledo
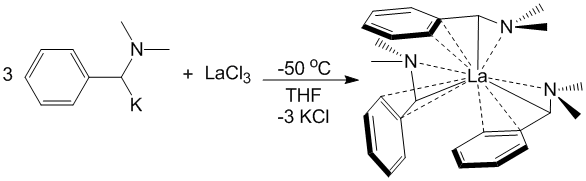
R R Yieldb [%] Ph 93 Ph CyN=C=NCy 74 Ph PhN=C=O 60 Ph CyN=C=O 54 Ph AdN=C=O 38c Ph 1-NaphN=C=O 76c Ph PhN=C=S 91 Ph (4-FC6H4)N=C=O 83d Ph (4-ClC6H4)N=C=O 83 Ph (4-BrC6H4)N=C=O 49 Ph (4-MeOC6H4)N=C=O 62 Ph (4-F3CC6H4)N=C=O 88 4-MeOC6H4 (4-BrC6H4)N=C=O 45 4-MeC6H4 (4-F3CC6H4)N=C=O 65