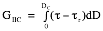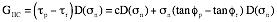41457-AC8
Slip Initiation on Frictional Fractures
Slip along pre-existing discontinuities and fracture propagation are key mechanisms for deformation and failure in rock masses. This is particularly the case under confinement, as tensile phenomena such as opening of fractures and mode I fracture propagation are prevented. For the past years the rock mechanics group at Purdue University has investigated experimentally and theoretically the dependence of the critical energy release rate GIIC on normal stress and on the frictional characteristics of a discontinuity.
A number of experiments was conducted first on acrylic, a material that, using photoelastic methods, allowed visualization of the stress field at the crack tip (i.e. at the boundary between the area of the fracture that had slipped and the area that had not); and later on gypsum, a rock model material with relatively low unconfined compression strength, and Portland cement mortar. In these tests, specimens made of two blocks were prepared and tested in shear. The two blocks were perfectly in contact with each other through a surface which had a low frictional strength on one half (weak surface) and a large frictional strength on the other half (strong surface). The fabrication procedure allowed for different frictional properties of the strong surface. Four different strong surface types were prepared: Type I with peak friction angle 51.4o, and residual friction 23.2o, c=0; Type II: peak 38.5o, residual 20.5o, c=0; Type III had the same friction values but with cohesion c = 1 MPa; and Type IV, with peak friction angle 23.5o, residual 22.3o, and c=0.85 MPa. The contact surface between blocks was loaded in shear at different normal stresses. From the experiments the critical slip, DC, required for the transition from peak to residual strength, and the critical energy release rate, GIIC, were measured.
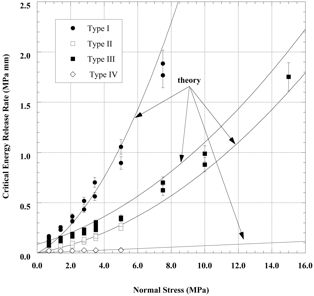
The critical energy release
rate GIIC is shown in the attached Figure. GIIC increases
with surface roughness and with normal stress but only in those cases where
there is a difference between peak and residual friction angles (Types I, II,
and III). The results obtained with a smooth surface (Type IV, with only
cohesion) show that GIIC is independent of normal stress. A
comparison between the Types II and III curves indicates that cohesion shifts
upwards the energy release rate curve but does not affect the rate of increase
with normal stress. These are very important observations because the magnitude
of GIIC is not a material property but depends on the frictional
characteristics of the slip surface and on normal stress. In compression, GIIC
depends on the shear stress drop from peak to residual and is: This formulation has been used
as a crack initiation criterion for shear fractures and it has been coupled
with an extended critical energy release rate formulation for both tensile and
shear cracks, such that initiation of a crack in tension or shear is the result
of two competing mechanisms. If the energy release rate at the tip of the
parent crack reaches first the critical energy release rate in tension, GIC,
then a tensile crack is produced. If it reaches first GIIC then a
shear crack initiates. The criterion has been implemented into the Displacement
Discontinuity Method code FROCK, which has been written by the PI. A number of
experiments with gypsum has been performed to investigate initiation and
coalescence from pre-existing closed (frictional cracks). In these experiments
two and three closed pre-existing frictional cracks are placed inside the
gypsum specimens, which are loaded in uniaxial compression. During loading
observations are made regarding crack initiation and coalescence. The types of
cracks induced: tensile and shear, the stress at which initiation occurs, and the
type of coalescence and coalescence stress are recorded. These observations have
been used to validate the model.