45286-G7
Reversible Self-Assembly of Boronic Acid-Containing Block Copolymers
Organoboron polymers are important precursors to materials with potential utility in catalysis, separations, and sensing applications and offer promise as electrolyte materials for batteries, blue emissive polymers, self-healing materials, precursors for functional polyolefins, and as potential surfactants for enhanced oil recovery. In order to more fully realize the potential of boronic acid-containing macromolecules in these fields, it is vital to expand the capability to prepare such polymers with precise control over topology, molecular weight, and composition. Our research is focused on devising methods for the synthesis of well-defined, water-soluble boronic acid copolymers from stable and easily manipulated boron-containing monomers. Additionally, we have employed highly efficient “click” chemistry techniques to further incorporate boron-containing moieties by postpolymerization modification.
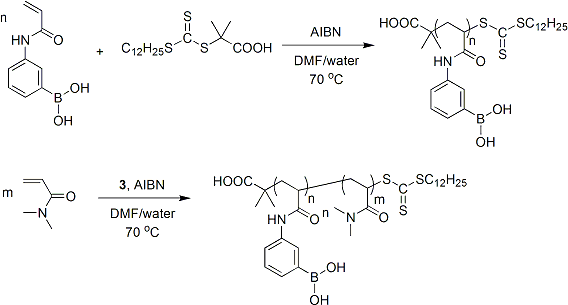
In the previous year of this project, we established a facile route to well-defined boronic acid (co)polymers from stable and easily manipulated boronic ester monomers. In the current year, we have successfully streamlined the synthetic process by developing routes to allow the direct polymerization of unprotected boronic acid monomers. In addition to expanding the range of functionality that can be directly incorporated into well-defined polymers, this route provides simplified access to a new class of “smart” block copolymers that demonstrate unique pH-, and more importantly, diol-responsive self-assembly. Boronic acid-containing block copolymers proved capable of forming well-defined micelles and higher order block copolymer aggregates by self-assembly in aqueous media. Dissociation of these aggregates was easily triggered by an increased concentration of model small molecule diols (e.g., glucose). Moreover, we have established routes by which boronic acid functionality can be incorporated into polymer end groups, which allows the preparation of a variety of dynamic covalent polymer assemblies based on reversible boronate ester formation.