

45567-AC1
Rhodium-Catalyzed Addition of Alkynes to Activated Ketones and Aldehydes
PRF# 45567-AC1
Rhodium-Catalyzed Addition of Alkynes to Activated Ketones and Aldehydes
Studies on ligand effects in the rhodium-catalyzed addition of alkynes to aldehydes and activated ketones are ongoing. Modification of the b-diketonate ligand has been shown to have a significant effect on the reaction rate and the yield of the reaction (eq. 1). Incorporation of electron withdrawing groups on the b-diketonate ligand significantly reduced the efficacy of the transformation, while electron-releasing groups had the opposite effect. Importantly, bulky t-Bu and Ph groups were well tolerated. The use of chiral b-diketonate ligands with bulky groups at these positions will next be explored.
The
expansion of transition-metal catalyzed nucleophilic addition reactions to the
addition of aryl and vinylboronic acids to 1,2-diketones and 1,2-ketoesters was
also explored. Several literature
reports describe rhodium metal complexes as excellent catalysts for the
addition of aryl and vinylboronic acids to aldehydes, but 1,2-dicarbonyl
electrophiles were conspicuously absent from these studies. Reaction conditions using catalytic
Rh(acac)(CO)2 and PPhCy2 provide excellent yields of
these addition products (eq. 2).
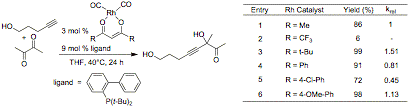 (1)
(1)
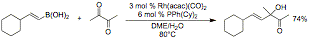 (2)
(2)