44314-AC7
Collagen-Inspired Polymers
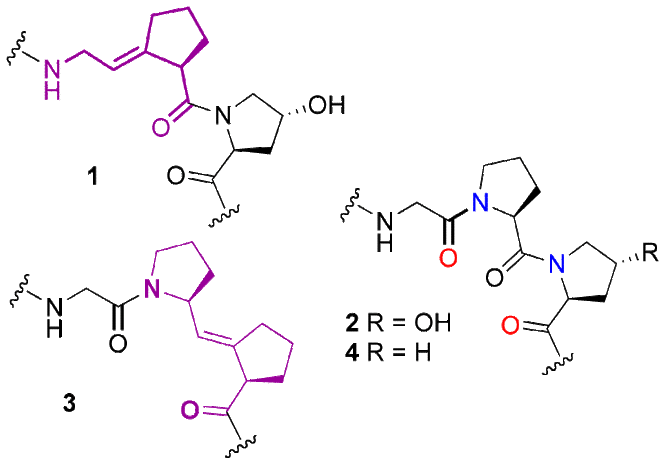
Collagen acts as a scaffolding material to support cells, and it is responsible for the elasticity and strength of the body. Stable polymers based on collagen may have interesting properties as materials, or they may serve as natural collagen replacement biomaterials for use in arthritis, wound, and bone repair. We designed a collagen Gly-Pro and Pro-Pro alkene isosteres (Figure). The amide bond between Gly and Pro in a host-guest peptide 1,1 and the amide bond between Pro and Pro in host-guest peptide 3 (N. Dai and F.A. Etzkorn, unpublished results) were replaced with (E)-alkene bonds to stabilize the collagen triple helix. The alkene bonds lock Gly-Pro or Pro-Pro in the trans conformation to prevent cis-trans isomerization. We expected the Gly-Pro substitution to lead to overall stabilization of the collagen host-guest peptide triple helix, while the Pro-Pro isostere was expected to be less stable due to the loss of an essential hydrogen bond in the triple helix.
The synthesis of a Ser-Y[(E)CH=C]-Pro isostere2 was modified to synthesize the Gly-Y[(E)CH=C]-Pro and Pro-Y[(E)CH=C]-Pro isosteres. Control peptides 2 and 4 of all natural amino acids and two peptides with the trans alkene isostere in the middle were synthesized.1 The stability of the collagen peptides was determined by the melting temperature (Tm) using circular dichroism (CD). The control peptide Ac-(Gly-Pro-Hyp)8-Gly-Gly-Tyr-NH2 2 had a Tm of 50.0 C, which is close to the literature value (47.3 C) for Ac-(Gly-Pro-Hyp)8-Gly-Gly-NH2.3 The peptide with an alkene isostere in the sequence, Ac-(Gly-Pro-Hyp)3-Gly-Y[(E)CH=C]-Pro-Hyp-(Gly-Pro-Hyp)4-Gly-Gly-Tyr-NH2 1, had a Tm of 28.3 C.1 Control peptide H-(Gly-Pro-Pro)10-OH 4 had a Tm of 31.5 C, which is close to the literature value.4 The peptide with an alkene isostere in the sequence, H-(Gly-Pro-Pro)3-Gly-Pro-Y[(E)CH=C]-Pro-(Gly-Pro-Pro)4-OH 3, had a Tm value of –22 C. The Tm values show that the alkene isostere peptides 1 and 3 form less stable triple helical structures than the native-like peptides 2 and 4. However, triple helix 1 was not nearly as destabilized as the peptide with the Pro-Pro or Pro-Gly4 alkene isosteres.2
Our hypothesis was not entirely correct, so the factors that influence the stability of the collagen triple helix are even more intriguing. The trans alkene isostere does not have the dipole moment of the amide bond, which may be a factor in stabilizing the collagen triple helix. Experiments are underway to investigate this hypothesis.
1 Ac–(Gly-Pro–Hyp)3–Gly-Ψ[(E)CH=C)]-Pro–Hyp–(Gly–Pro–Hyp)4–Gly–Gly–Tyr–NH2,
Tm
= 28.3 °C 2 Ac–(Gly–Pro–Hyp)3–Gly–Pro–Hyp–(Gly–Pro–Hyp)4–Gly–Gly–Tyr–NH2,
Tm
= 50.0 °C, ΔTm = –21.7 °C 3 H–(Pro–Pro–Gly)4–Pro-Ψ[(E)CH=C)]-Pro–Gly–(Pro–Pro–Gly)5–OH,
Tm
= –22 °C 4 H–(Pro–Pro–Gly)4–Pro–Pro–Gly–(Pro–Pro–Gly)5–OH,
Tm
= 31.5 °C, ΔTm =
–53.5 °C References 1. Dai,
N.; Wang, X. J.; Etzkorn, F. A., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, (16), 5396 - 5397.
2. Wang,
X. J.; Hart, S. A.; Xu, B.; Mason, M. D.; Goodell, J. R.; Etzkorn, F. A., J.
Org. Chem. 2003, 68, (6),
2343-2349.
3. Persikov,
A. V.; Ramshaw, J. A.; Kirkpatrick, A.; Brodsky, B.,Biochemistry 2000, 39, (48), 14960-7.
4. Jenkins,
C. L.; Vasbinder, M. M.; Miller, S. J.; Raines, R. T., Org Lett 2005, 7, (13), 2619-22.