43703-AC1
C-C-C N-Heterocyclic Carbene Pincer Complexes: A General Method of Preparation Critical for Applications in Catalysis
Abstract: Upon heating Zr(NMe2)4 (1.1 equiv), 1,3-bis(N-butyl-imidazolium)benzene diiodide (1.0 equiv) and toluene, analytically pure [Zr(CCC-NHC-pincer ligand)I2(NMe2)] was obtained upon cooling, which was found to be an efficient intramolecular hydroamination/cyclization catalyst.
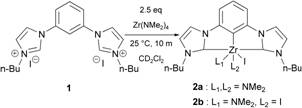
Our previous methodology (Scheme 1) exploited the basicity and electrophilicity of Zr(NMe2)4 to activate the three C-H bonds of ligand precursor 1 for coordination to the Zr metal. Although this method rapidly produced the desired complex, it employed an excess of Zr(NMe2)4, produced a mixture of coordination spheres at Zr (2a and 2b) and did not lead to ready separation of the Zr pincer product from the excess reagent.
Scheme 1. Original
synthesis with excess reagent.
The use of a stoichiometric amount of Zr reagent was highly
desired. Subliming Zr(NMe2)4
prior to use, employing higher boiling solvents and longer reaction times
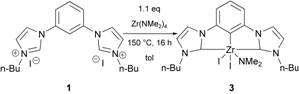
provided the desired complex in high yield and purity. Combining the bis(imidazolium) salt 1, Zr(NMe2)4
(1.1 eq), toluene and heating in a sealed vessel produced a homogeneous
reaction mixture (Scheme 2). Metallation
was found to proceed efficiently and quantitatively as observed by 1H
NMR spectroscopy. Metallation was
incomplete at 150 minutes, but longer reaction times were found to be
satisfactory. Upon scaling up the
reaction an additional advantage was found.
At the completion of the reaction the desired complex 3 precipitated upon cooling in
analytically pure form (1.8 g, 67%) as shiny yellow crystals. The only by-product of reaction was the
volatile and soluble Me2HN.
The slight excess of Zr(NMe2)4 remained in
solution.
Scheme 2. Improved
metallation procedure for triple C-H activation.
1H
and 13C NMR spectroscopic analysis of the precipitated yellow
crystals confirmed that pure CCC-NHC pincer 3 was synthesized. X-ray
quality crystals of 3 were selected
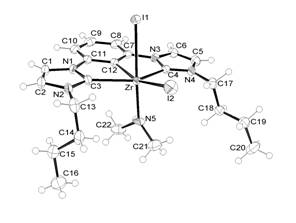
from the precipitate. An ORTEP® view of
complex 3 is presented in Fig
1. In the solid state zirconium adopts a
distorted octahedral geometry. The Zr-C(carbene) distances, 2.367(3) and
2.362(3)Å, are similar to previous reports of pincer NHC complexes of
Zr,10b, and shorter than non-chelated
NHC – Zr distances (2.43 - 2.46 Å). The
Zr-C12(aryl) distance is 2.310(3) Å, slightly shorter than the complex 2b,
which contained an equatorial amido group.
The axial Zr-I1 distance, which is trans to NMe2, is 3.0038(4) Å,
demonstrating a stronger trans influence for the amido group compared to the
aryl group, since the equatorial Zr-iodide
distance, trans to Ar, is 2.8431(4) Å. The Zr-N (amido) distance is 1.986(3)
Å. The crystal shows evidence of a
slight axial/equatorial disorder that was modeled at a 94:6 occupancy. Additional data are listed in Fig 1.
Fig. 1. ORTEP® representation of the molecular structure of 3 (major isomer illustrated, 94%).
Selected geometric data: Zr-C12, 2.310(3) Å; Zr-C3, 2.367(3) Å, Zr-C4, 2.362(3)
Å; Zr-I1, 3.0038 Å; Zr-I2, 2.8431(4) Å; Zr-N5, 1.986(3) Å C12-Zr-C3, 68.20(11)°; C12-Zr-C4, 68.28(11)°; C12-Zr-I1, 79.88(7)°; C12-Zr-I2, 162.66(7)°;
C12-Zr-N5, 107.11(12)°; C3-Zr-C4,
136.40(11)°; I1-Zr-I2, 83.278(11)°; N5-Zr-I1, 172.86(10)°.
CCC-NHC
zirconium pincer complex 3 was
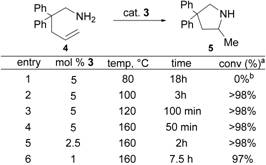
assayed for hydroamination activity against 2,2-diphenyl-4-pentenamine 4. The results of these experiments are
summarized in Table 1. All of the
catalytic reactions were conducted in deuterated solvent, and the reaction
progress was monitored by 1H NMR spectroscopy.
At 80°C the CCC-NHC pincer zirconium complex 3 did not show any catalytic activity (Table 1, entry 1). Changing the solvent to toluene and
increasing the temperature from 80° to 100°C (entry 2) revealed excellent
catalytic activity with 2,2-diphenyl-4-pentenamine 4 quantitatively converted into the corresponding pyrrolidine 5 after 100 min. Conducting the reaction in a sealed NMR tube
and increasing the temperature to 120°C (entry 3) and 160°C (entry 4) yielded
the cyclized pyrrolidine 5 in
quantitative yield more rapidly (100 min and 50 min). The catalyst loading could be reduced to 2.5
and 1 mol% (entry 5 and 6) with success.
Table 1. Optimization of hydroamination conditions.
a All conversions were determined by 1H NMR. b
solvent = C6D6.
All others: solvent = C7D8.
From the
series of hydroaminations with 4,
the optimized condition of 5 mol% catalyst loading in toluene-d8 under reflux
was selected to study the scope and limitation of catalyst 3 (Table 2).
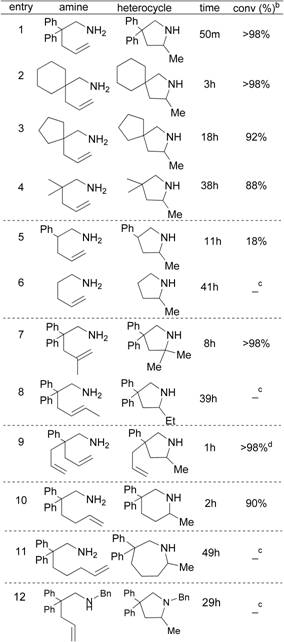
Table 2. Substrate survey of hydroamination catalytic
activity.a
a 5 mol% of 3,
Toluene-d8, 160 °C. b Conversion determined by 1H
NMR spectroscopy. c No
reaction. d Diastereomeric ratio: ~1:1.
In
conclusion, we report herein an efficient method for preparing analytically
pure and on large-scale Zr CCC-NHC pincer complex 3. Complex 3 has been shown to have excellent
catalytic activity in the hydroamination/cyclization of unactivated
alkenyl-amine yielding pyrrolidines and piperidines.