45427-AC7
Water as the Preferred Solvent for Lewis Acid-Catalyzed Free Radical Polymerization and Initiation of Spontaneous 'Charge-Transfer' Polymerization
Water as the Preferred Solvent for Lewis Acid-catalyzed Free Radical Polymerization
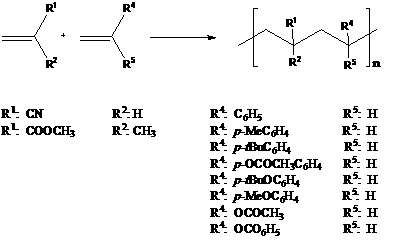
Lewis acids have been established as favoring the formation of 1:1 alternating copolymers from the free radical polymerization of electron-rich monomers with electron-poor monomers. They act by complexing to the lone electron pair in the electron-poor monomers, thereby making it even more electron-poor, which enhances the tendency to alternation. In recent years Lewis acids have been found to function in numerous aqueous systems. 1-5 We utilized Irgacur 809 as initiator.
Results-acrylonitrile
Acrylonitrile
was copolymerized with styrene in presence of water and zinc bromide. As the
latter rose from 5 mmole to 20 mmole, yields and the copolymer molecular weight
increased. NMR showed that these were random copolymers. Other styrenes, normally p-methylstyrene, p-t
butylstyrene, p-t butoxystyrene and p-acetoxystyene, gave high yields and high molecular weights when
20 mmole of zinc bromide and 55 mmol of water were used. Similar results were
found for vinyl acetate and vinyl benzoate. (Table 1) Table SEQ Table \* ARABIC 1: Initiated copolymerization of acylonitrile
with different comonomers in water
Monomer 1 mmols Monomer 2 mmols mmols ZnBr2 ml water Reaction time/ remarks Yield % Acrylonitrile 5 Styrene 5 5 1 -2h irradiation -alternating, low MW 12 5 5 10 1 -2h irradiation -alternating, low MW 41 5 5 15 1 -2h irradiation -random, high MW 55 5 5 20 1 -2h irradiation -random, high MW 52 5 5 25 1.25 -2h irradiation -random, high MW 56 5 5 20 2.5 -2h irradiation -alternating, low MW 14 5 5 20 5 -2h irradiation -alternating, low MW 9 5 5 20 2.5 -20h irradiation -alternating, high MW 82 5 p-Methylstyrene 5 20 1.25 -2h irradiation -random, high MW 53 5 p-t-Butylstyrene 5 20 1.25 -2h irradiation -random, high MW 65 5 p-Methoxystyrene 5 20 1.25 -2h irradiation -homopolymer, poly-methoxystyrene 100a 5 p-Butoxystyrene 5 20 1.25 -2h irradiation -random, 44 5 p-Acetoxystyrene 5 20 1.25 -2h irradiation -random, high MW 92 Results –
Methyl methacrylate Very similar results
were obtained when methyl methacrylate replaced acrylonitrile as electron-poor monomer.
The trends of yields with the amount of water and zinc bromide were the same.
Again the copolymers were random, for which the same explanation as for
acrylonitrile is offered. (Table 2) Table SEQ Table \* ARABIC 2: Initiated copolymerization of methyl methacrylate
with different comonomers in water
Monomer 1 mmols Monomer 2 mmols mmols ZnBr2 ml water Reaction time/ remarks Yield MMA 5 Styrene 5 5 1 -2h irradiation -low molecular weight 9 5 5 10 1 -2h irradiation -low molecular weight 12 5 5 15 1 -2h irradiation -high molecular weigh 74 5 5 20 1 -2h irradiation -high molecular weight 95 5 5 25 1.25 -2h irradiation -high molecular weight 83 5 p-Methylstyrene 5 20 1.25 -2h irradiation -random, high molecular weight 78 5 p-t-Butylstyrene 5 20 1.25 -2h irradiation -random, high molecular weight 65 5 p-Methoxystyrene 5 20 1.25 -2h irradiation -homopolymer, poly-methoxystyrene 78 5 p-Butoxystyrene 5 20 1.25 -2h irradiation -random, 69 5 p-Acetoxystyrene 5 20 1.25 -2h irradiation -random, high molecular weight 80 5 Vinyl Acetate 5 20 1.25 -2h irradiation -random, high molecular weight 34 5 Vinyl Benzoate 5 20 1.25 -2h irradiation -random, high molecular weight 40 Results
–Spontaneous copolymerization If no photoinitiator
was used and the reaction mixtures were stirred at room temperature for 2-3
days, spontaneous copolymerization occurred. All of the styrenes gave high
yields of high molecular weights copolymers, whose alternation is under
investigation. The sole exception is p-methoxystyrene,
which as before gave cationic homopolymerization. Under these conditions the
vinyl esters gave no copolymers. (Table 3) Table SEQ Table \* ARABIC 3: Spontaneous copolymerization of
acrylonitrile with different comonomers in water
Monomer 1 mmols Monomer 2 mmols mmols ZnBr2 ml water Reaction time/ remarks Yield % Acrylonitrile 5 Styrene 5 20 1.25 -3d, rt. -high molecular weight 70 5 5 20 2.5 -3d, rt. -high molecular weight 61 5 -- -- 1.25 -3d, rt. 0 5 p-Methylstyrene 5 20 1.25 -1d, rt -high molecular weight 52 5 p-Methylstyrene 5 20 1.25 -3d, rt. -high molecular weight 76 5 p-t-Butylstyrene 5 20 1.25 -3d, rt. -high molecular weight 70 5 p-Methoxystyrene 5 20 1.25 -1d, rt -homopolymer, poly-methoxystyrene 96a 5 p-Acetoxystyrene 5 20 1.25 -1d, rt -high molecular weight 98 5 p-Acetoxystyrene -- -- 1.25 -10d, rt 0 5 p-Acetoxystyrene 5 20 2.5 -1d, rtt 0 5 p-Acetoxystyrene 5 20 5 -5d, rt 0 5 Vinyl Acetate 5 20 1.25 -5d, rt 0 5 Vinyl Benzoate 5 20 1.25 -5d, rt 0 a yield calculated in regard with the p-methoxystyrene Reference: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.