ACS PRF | ACS
All e-Annual Reports

43108-B4
Catalytic Organic Molecular Imprints
Our research efforts are aimed at the generation of organic, polymeric “molecular imprints” with improved—and novel—catalytic activities. Towards this goal, we have been exploring two systems: The first involves a lactonization reaction, the second an aldol condensation. Both of these systems incorporate two features intended to enhance the catalytic activity of the imprints obtained: One, each employs a covalent or “stoichiometric-noncovalent” bond between functionalized monomer and template; and two, each incorporates a nucleophile into the catalytic mechanism. Covalent and stoichiometric-noncovalent imprinting allow for more precise positioning of the template (and thus of the analogous substrate) within the polymeric matrix, while direct participation of a catalytic nucleophilic functionality—a mechanistic feature that can lead to huge rate accelerations in intramolecular model systems—should lead to enhanced rates.
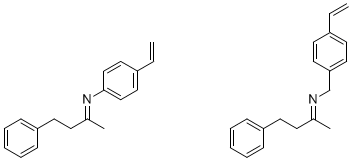
During the past year, we did not pursue the lactonization project. However, we have continued to work on the aldolase system, and have recently generated imprints against the following two imine templates (which were prepared from benzylacetone and either 4-vinylaniline or 4-vinylbenzylamine, respectively, in the presence of molecular sieves as a dehydrating agent1):
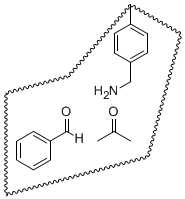
We are now in the process of hydrolyzing the imine linkage within the molecular imprint to yield a material that we hope will catalyze the corresponding aldol condensation between acetone and benzaldehyde (the benzylamine-containing imprint is illustrated with the substrates bound): Finally, inspired by an antibody catalyst reported by the Tellier group,2 we have begun work on the generation of a molecular imprint for the catalysis of an allylic isomerization reaction. In this system, a stoichiometric-noncovalent complex between an amidine template and vinylbenzoic acid provides the basis for the imprint. 1Kyba, E.P. “An Improved Synthesis of Ketamines,” Org. Prep. Proc. 1970, 2, 149-156. 2Gonçalves, O.; Dintinger, T.; Lebreton, J.; Blanchard, D.; Tellier, C. “Mechanism of an antibody-catalysed allylic isomerization,” Biochem J. 2000, 346, 691-698.