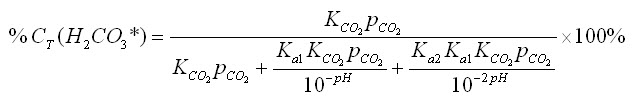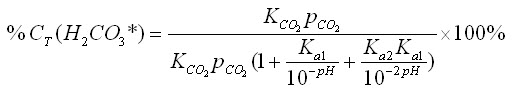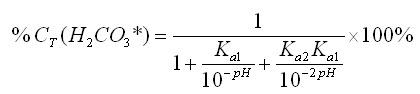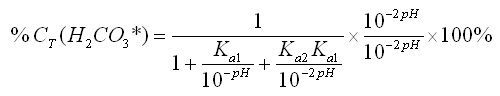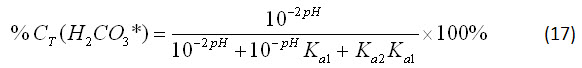Carbon Speciation in a Closed System
In a closed system, we can more specifically analyze the relative concentration of each species. Since a closed system cannot lose molecules from solution, the total concentration of all species of a molecule (CT) must remain constant, even if relative amounts of species differ.
Since equation 15 must remain a constant value in a closed system, we can consider the percent relationship between the three concentrations. For carbonic acid, this relationship is
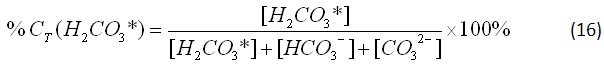
By substituting equations 12-14 into equation 16, we can further simplify it: