Background
CO2 and Ocean pH
To determine the relationship between pH, atmospheric carbon dioxide and the relative concentrations of carbonate species, a detailed analysis of the equilibrium equations is required.
Atmospheric carbon dioxide exists in a dynamic equilibrium with dissolved carbon dioxide, represented in equation 1:
The equilibrium expression is
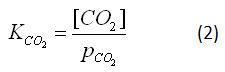
where [CO2] is the concentration of dissolved carbon dioxide and pCO2 is the partial pressure of atmospheric carbon dioxide. It is important to note that equilibrium constants are dependent on the matrix in which the reaction occurs. Thus, the equilibrium constant is dependent on temperature, salinity and the presence of other ions in solution, as well as other factors.