Reports: AC4
45801-AC4 Bond Compression in Triptycene-Containing In-Cyclophanes
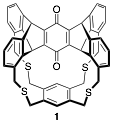
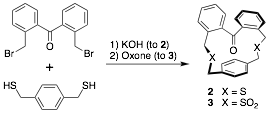
in-Cyclophanes. This award chiefly supports the synthesis of highly strained in-cyclophanes with compressed covalent bonds. In the last year, the most important result is the synthesis of the first in-ketocyclophane. Our initial efforts focused on the synthesis of triptycene-based cyclophane with an in-ketone (1), as suggested by the title of this award, but all attempts to perform the final macrocyclization, which required the formation of four C-S bonds, were unsuccessful.
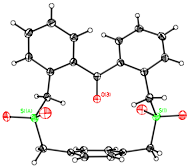
Extensive computational studies revealed that a simpler, alternative target might possess an in-ketone. B3PW91/6-31G(d) calculations indicated that the benzophenone-containing cyclophane 2 should have the ketone lying parallel to the basal aromatic ring, but the conformational restrictions imposed by converting the thioethers of 2 to the sulfones in cyclophane 3 should cause the molecule to adopt a C2-symmetric conformation with the ketone pointed directly at the aromatic ring. Compounds 2 and 3 were prepared as indicated below, and their single crystal X-ray structures were determined.
The X-ray structure of compound 3 verified the computational prediction. Compound 3 possesses crystallographic C2 symmetry with the ketone projected toward the base of the cyclophane, and the in-ketone oxygen is 2.91 from the center of the basal aromatic ring. Although the carbonyl bond distances in compounds 2 and 3 are not significantly different, but infrared carbonyl stretching frequency in 3 (1658 cm-1) is enhanced by 5 cm-1 when compared to that of 2 (1653 cm-1), an indicator of modest steric compression.